
Chest and Abdominal Pain
Abdominal and Chest pain has been said to have similar pain sensations as that of a heart attack. In fact, many people who are not aware of the different factors that can cause similar excruciating pain often begin to think the worst leaving them in a state of unwavering fear that makes them believe they are having a heart attack. If you begin experiencing dreadful chest pains or abdominal pain please make sure to request immediate medical help especially if the symptoms involve:
Food Safety Tips to Avoid Food Poisoning
Food illness is a risk during this time of year when everyone is celebrating and constantly making delicious food. So how can you safeguard yourself and others you care about from accidental food poisoning? Here are some food safety measures that can help save you from becoming sick:


Appendicitis occurs when the appendix is inflamed, typically due to an infection or a blockage caused by stool, a foreign body or other reasons. Appendicitis can be extremely serious and, in rare instances, even deadly. Although it is not clear why the body has an appendix – in fact, it is not even known why it exists – if the organ fails, there can be serious consequences.
Pain associated with appendicitis can be intense to the point that it is totally incapacitating. This appendix inflammation is an emergency situation that must be treated as soon as possible to avoid the possibility of a possible burst of the organ.When this happens, bacteria spreads throughout the abdomen and can lead to death. Here are some of the signs of appendicitis that can help you act quickly and reach the nearest emergency medical facility as soon as possible.
Pain from appendicitis usually strikes the right side of the abdominal cavity. However, in the early stages, people often ignore the pain. The condition is caused by a blockage and inflammation of the appendix lining and occurs less frequently than 10 percent of the time. However, it can cause extreme pain when it hits. If not treated promptly, it can lead to infection as well as severely restricting blood flow.
Appendicitis can cause several different symptoms. Some people will experience them differently than others, but all of them must be taken seriously, so you must seek medical treatment right away.In as little as 48-72 hours after symptoms occur, an appendix can rupture.
Dull pain in the area of the belly button that changes near the lower right portion of the stomach is a very common symptom of appendicitis. In most cases, the pain increases steadily and without subsiding.
The path of the pain is also very important. If the pain moves from your navel to the area over your appendix, this could indicate the imminence of an appendicitis attack – possibly as soon as 12-24 hours. In most cases, the appendix is located at the lower right portion of the abdomen, about a third of the way between the belly button and the hip bone. If the appendix is painful to touch, get to an emergency room as soon as possible. Also be aware of “rebound sensitivity.” When you release after pressing, you will feel pain right away.
If you have been feeling discomfort, touch the area gently and see if it feels tender. Pay close attention if the discomfort gets worse when you sneeze, cough, or take deep breaths. If the discomfort worsens and is accompanied by nausea, constipation, or abdominal swelling, or if you are unable to pass gas, you should seek medical attention immediately. It is critical not to use any pain medication if you have any reason to believe you are suffering from appendicitis. The reason for this is because drugs have the potential to mask your discomfort, making it more difficult for your doctor to make an appropriate diagnosis. It is also critical that you avoid taking any laxatives, as this could result in an abscess or a rupture.
If you feel that you or a loved one has appendicitis, hurry to your nearest emergency room as soon as possible. Failure to do so could lead to a ruptured appendix, which could be life-threatening. We have a high level of expertise treating people with appendicitis at Kingswood ER, so let us take care of your health needs.
Back pain, particularly lower back pain, is one of the most frequent health problems among adults in the United States. According to the American Physical Therapy Association, over two-thirds of Americans suffer from lower back discomfort, with 37% not seeking treatment.
The pain can range from minor annoyance to severe, ongoing agony. Back discomfort, if left untreated, can make it difficult to walk, stand, or run comfortably, along with affecting a person’s general mood and well-being.
The good news for those who suffer from chronic, acute back pain is that it may often be treated and eliminated in a couple of weeks. In addition, there are a number of lifestyle adjustments you could do to prevent back discomfort from returning.
Back discomfort can be caused by a variety of factors. Acute back pain is caused by overuse or an injury, such as a herniated disc, muscular strain, or sciatica, and normally lasts shorter than six weeks. Chronic back pain, which lasts longer than three months and is less prevalent, is often caused by a spinal problem such as degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis.
Risk factors can also play a role in the development of back pain. Back pain can be caused by a multitude of reasons when an injury hasn’t happened such as:
Before you put any undue stress on your back that could worsen your symptoms, it’s a good idea to get the advice of a medical practitioner to assist diagnose the problem.
Exercise – Working out when in pain may seem paradoxical, but light aerobic movement is sometimes just what a tight or sore back needs. In fact, prolonged bed rest or inactivity might aggravate acute back pain. In addition, increase blood flow to the muscles in the lower back, hips, and buttocks by walking, riding a stationary bike, or swimming.
Medication – Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are two over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicines that might assist manage pain while you’re at work or attempting to sleep. Just keep in mind that these medications merely disguise the symptoms, not cure them. In addition to pain pills, you may want to consider using an ice pack or heating pad to alleviate discomfort and swelling in the affected area.
Physical Therapy – If you’re having problems doing exercises on your own because of severe pain or limited mobility, a physical therapist can help you get started by guiding you through strength exercises tailored to your needs. Consult your primary care physician about starting physical therapy on your own.
Change Up Your Sleep Routine – Yes, even how you sleep can aggravate or alleviate your problems. To keep your spine straight, sleep on your side with a pillow or folded blanket between your legs. If sleeping on your side is difficult for you, try sleeping on your back with a cushion or blanket under your legs to keep them raised. This keeps the spine’s normal bend throughout the night.
Stay Active – More than half of back pain sufferers are believed to spend the majority of their workday seated. Staying physically active is one of the simplest ways to avoid back discomfort caused by inactivity for long periods of time. It could be as easy as going for a daily stroll during your lunch break or going for a weekend excursion, as long as your muscles and joints are moving on a regular basis.
Change Your Diet – Being overweight raises your risk of lumbar muscle strains because your lower back bears so much of your body weight. Improving your eating habits can help you lose weight, which can help prevent future back pain.
Reduce Stress – Remember that your mind and body work together. When you’re anxious, your entire body feels it, and stiff back, neck, and shoulder muscles are common side effects. Yoga is frequently suggested because it relieves stress while also improving core strength and flexibility. You might also attempt deep breathing or find a regular relaxing pastime, such as writing, reading, or listening to music.
Improve Your Posture – Remind yourself to sit up straight if you spend lengthy periods of time at a computer. You invite unpleasant strain and stress on the muscles by allowing your shoulders, neck, and spine to slump over a keyboard or phone. If you have difficulties remembering to keep your back upright, consider adding a lumbar cushion to your chair.
While acute back pain may typically be controlled and avoided by a variety of exercises and lifestyle changes, many more serious back problems necessitate prompt medical attention. The team at Aether Health – Kingwood ER delivers skilled emergency care for fractures, sprains, and other back injuries, and patients do not have to wait as long as they would at a large hospital or other medical facility.

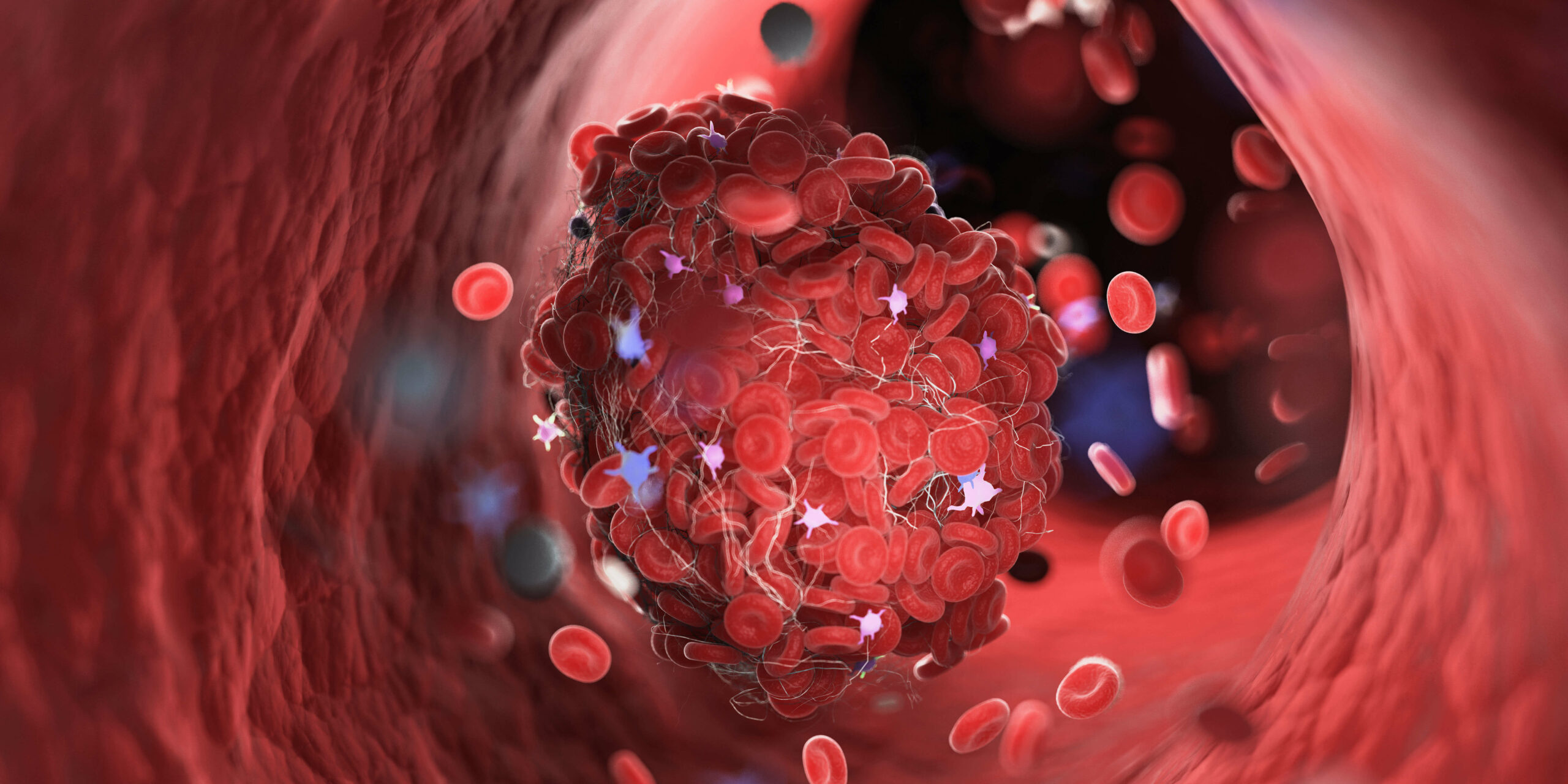
Blood clots are dangerous and can even be fatal. That is why, if you experience symptoms of a clot, you should seek medical attention as quickly as possible at your nearest emergency care facility. Some of the more prevalent indications are listed below.
Blood clots form in one of the body’s deeper veins, causing this condition. While they are most commonly found in the legs, they can also form in the abdomen, arm, and even the brain. Swelling, soreness, bluish or reddish coloring of the skin, and a sense of warmth in the affected area are all symptoms.
A pulmonary embolism is a dangerous consequence of deep vein thrombosis that occurs when a clot reaches the lungs. Chest pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply, a racing heart, an unexplained cough or coughing up blood, or shortness of breath are all symptoms. If you think you could have a pulmonary embolism, go to the nearest emergency medical center immediately.
There are a number of factors that can raise the risk of blood clots. Immobility caused by extended sitting, hospitalization or surgery, wearing a cast, or suffering from a medical disease such as cancer or rheumatoid arthritis are examples. Varicose veins, old age, a family history of clots, obesity, and others are all risk factors.
If you are experiencing signs of blood clots, please do not hesitate to go to the nearest emergency room as soon as possible. If you’d like to learn more about us or the services we provide, please contact us.
The better you understand your breathing issues, the more likely you are to be able to control them. Knowing the origin of the problem, in addition to a correct diagnosis and an effective treatment plan, can go a long way toward assisting you in returning to the productive, active life you enjoy. These are just a handful of the more typical causes for this problem.
Breathing issues can manifest themselves in a variety of ways. For example, frequent sinusitis attacks may make it difficult to breathe through your nose for up to two weeks. You could also just have a cold, and in a few days, you’ll be able to breathe normally again.
Some problems, on the other hand, are long-term. Asthma, allergies, chronic sinusitis, and other conditions are among them. They can cause a variety of additional symptoms, including watery and itchy eyes, nasal and chest congestion, coughing, wheezing, and more. COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, affects millions of people in the United States.
When determining the source of respiratory issues, doctors investigate a variety of criteria. Family medical history, the patient’s medical history, a physical exam, and a variety of additional tests are among them. If you have this problem, you should get a lung function test and a chest X-ray. If sinusitis appears to be the culprit, your sinuses may be tested using a specific CT scan.
Of course, the type of treatment you receive will be determined by the source of your breathing problems. Allergy treatments such as decongestants and antihistamines can be highly useful, and steroids are occasionally prescribed to relieve the inflammation associated with sinusitis.
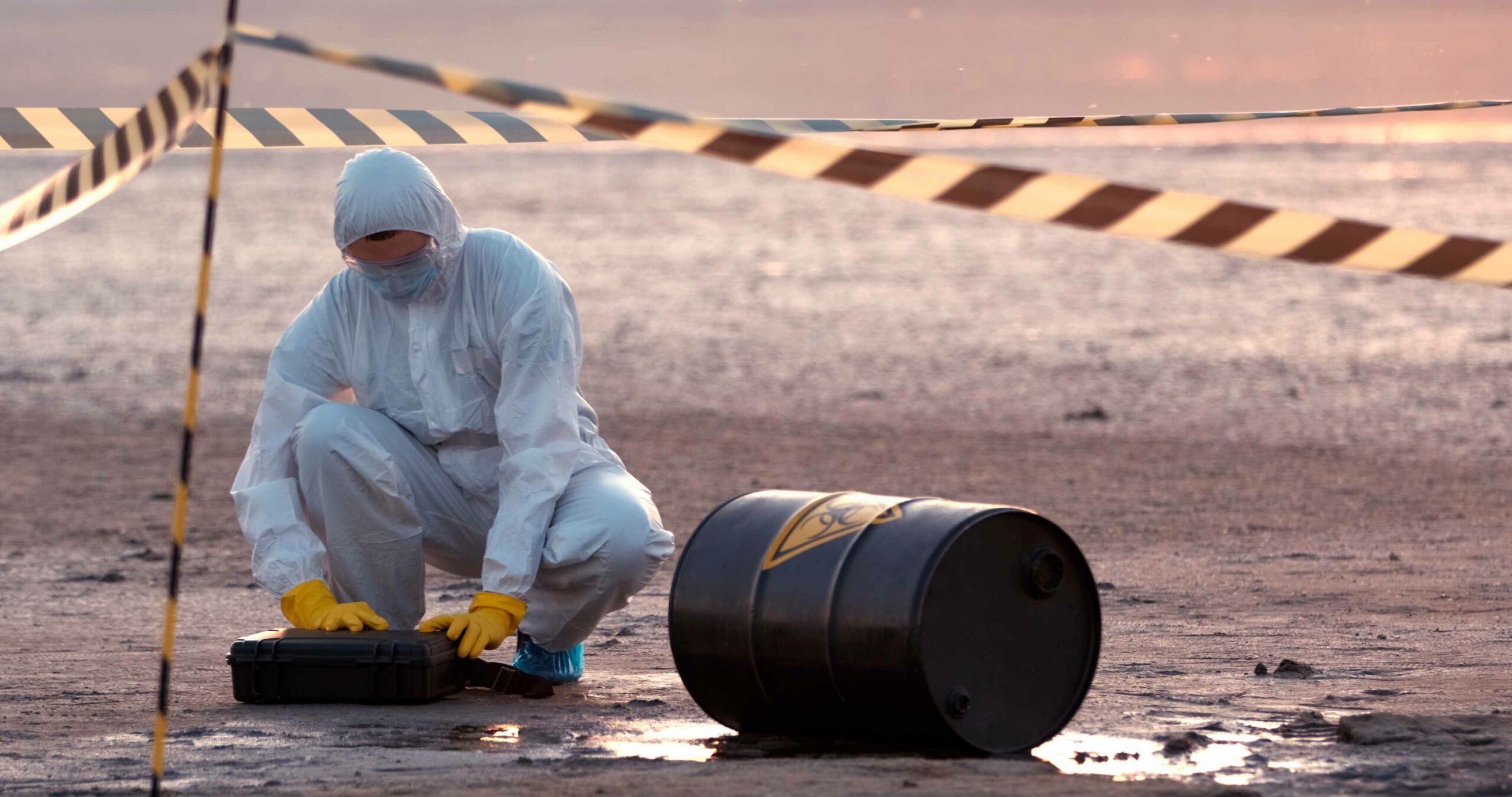


Chemical exposure, regardless of its severity, is something that no one wants to go through. Cleaning products, such as bleach, might cause modest symptoms in some people.
If inhaled, it might cause brief pain and coughing, among other things. Chemicals can also cause life-threatening side effects, necessitating a trip to the emergency department. The truth is that different chemicals have varied effects on the body. Almost any bodily function can be negatively impacted. Chemicals come in three different forms: solid, liquid, and gas. The following are some of the more serious adverse effects that people may encounter as a result of chemical exposure.
Some chemicals can cause eyesight loss that is either temporary or permanent. Arsenic is one substance that might induce this disease. Although blindness is not life threatening in and of itself, it is frequently accompanied by more serious symptoms.
Chlorine is a chemical that, when used in little amounts, does not cause serious harm. However, if this chemical is inhaled in large amounts, it can cause fluid to develop in the lungs. If not treated, this can lead to pneumonia, which can be fatal if not addressed.
Chemical inhalation can cause a variety of breathing issues, ranging from slight to severe. In the most extreme situations, the victim may be unable to breathe at all.
In severe circumstances, chemical exposure might render a person immobile. The paralysis may only affect a portion of the body in some cases. In some situations, the entire body is rendered immobile.
One of the most significant symptoms that someone exposed to toxins can encounter is loss of consciousness. This can happen as a result of exposure to certain substances, such as hydrogen sulfide.
Anyone who comes into contact with a toxic substance in large levels can die. This can happen as a result of asphyxia or because the body begins to shut down. If you or a loved one is experiencing minimal to mild chemical poisoning symptoms, get medical attention immediately. Exposure symptoms may appear mild at first, but they can quickly escalate.
We certainly hope that you or someone you love will never have to suffer from severe chemical symptoms. If this would ever happen, though, we want you to know that we are fully equipped to help you since we offer advanced emergency room services at all our Texas Emergency Rooms. We are honored to be there for you when you need the highest quality of medical care and quick attention.
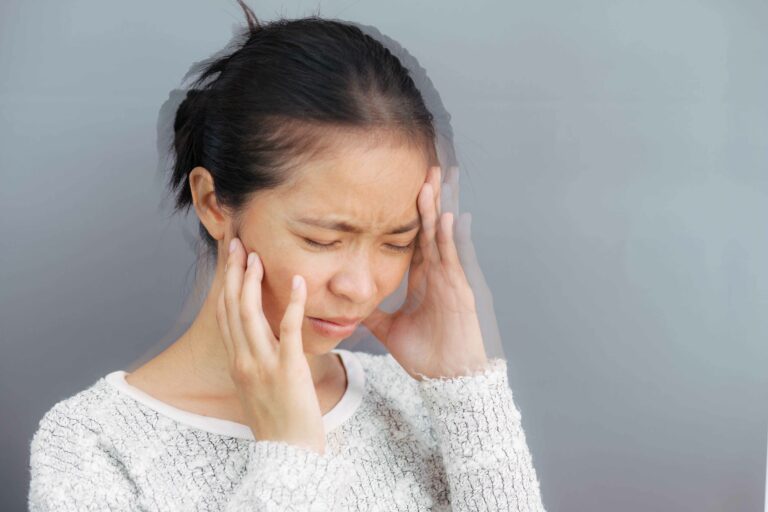
Dizziness is a symptom of a variety of diseases, not a sickness or problem in and of itself. While dizziness has a variety of symptoms, some of them are modest and only last a short time. Others, on the other hand, should be taken very seriously, and you should get to an emergency medical center as soon as possible. Here are some of the causes of dizziness, as well as warning indications that you should consult a doctor right away.
Symptoms of dizziness include:
When speaking with your doctor, it’s critical to describe the sensations you’re having as precisely as possible so that the right diagnosis can be established.
Dizziness can be caused by anything from motion sickness to a more sophisticated issue like an inner ear disorder. It can be an indication of a very significant heart or blood vessel problem in some cases. These are only a few of the causes of dizziness.
Heart Attack: Dizziness symptoms can be caused by a decrease in blood supply to the brain, which could be an indication of a heart attack. If you lose consciousness suddenly, it’s usually because your brain’s blood supply has been severely cut off. If you or a loved one passes out or loses consciousness, seek medical help as soon as possible.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Every system in the body, including the brain, goes into reserve mode when blood sugar levels are low. This is your body’s technique of conserving energy and may cause you to feel lightheaded or dizzy. Drinking some juice may help alleviate symptoms in certain circumstances, but it’s essential to have your blood sugar levels checked as soon as possible.
Motion Sickness: When traveling by automobile, boat, plane, or train, many people get motion sickness. Dizziness is a symptom that your body’s sensory organs are providing mixed signals to your brain in this scenario. People may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, and nausea as a result of their bewilderment. If you know you’re prone to motion sickness, you can take prescription or over-the-counter medication to help prevent symptoms.
Hypotension: Low blood pressure is known as hypotension. Low blood pressure is generally preferred to high blood pressure, but it might make you feel weary or dizzy if it drops too low. Hypotension might be an indication of an underlying problem in several situations. Hypotension can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Dehydration: Your blood volume can drop if you don’t drink enough fluids. This decreases your blood pressure and prevents enough blood from reaching your brain, leaving you dizzy or lightheaded. A glass of water may be plenty, but if you haven’t eaten or drank enough for several days, it will take more. In severe circumstances, you may require an intravenous fluid infusion from your doctor. Dizziness can also be caused by the following factors:
After a short period of time, dizziness normally goes away on its own. If you get a dizzy spell, stay away from smoke and caffeine and sit or lie down until it passes. Contact your doctor if the spell is accompanied by hearing loss, a strong headache, nausea, or vomiting.
Have someone take you to the nearest emergency medical center as quickly as possible if you are having shortness of breath, any change in speech or vision, limb weakness, or chest pain.
Dizziness isn’t a symptom you should dismiss because it could indicate a more serious problem. If you have any questions or want immediate treatment, Aether Health – Kingwood ER is available day and night. We provide a wide range of services to assist you and your family in times of need.
Dizziness isn’t a symptom you should brush off, as it could be the sign of a more serious condition. If you have questions or need immediate treatment, your nearest Complete Care location is ready to help, no matter the time of day or night. We offer a variety of services to help you and your family in your time of need.

Anyone who has had a foreign object in their eye knows how frightening it can be. While you should be able to remove the object at home most of the time, there may be occasions when you need to go to an emergency room to have it properly removed by a medical specialist. Here’s some advice on how to deal with this issue in the safest way possible.
Bones are rigid, but they can bend or “give” somewhat when a force is applied to them. However, if the power is excessive, the bones will snap, much like a tree limb twisted too far.
The severity of a fracture is usually determined by the force that caused it to break. If the breaking point of a bone is only slightly exceeded, the bone may crack instead of breaking completely. The bone may shatter if the force is too great, such as from a gunshot or a car accident. An “open” fracture occurs when a bone breaks in such a way that pieces from the bone break through the skin or a lesion pierces down to the damaged bone. Once the skin has been penetrated, infection can develop in both the laceration and the bone.
The following are some of the most common types of fractures: Fracture that is stable. The shattered ends of the bone are aligned and only slightly misaligned. An open compound fracture. The skin might be penetrated by the bone or ruptured by an impact that fractures the skin at the time of the fracture. This does not always imply that the bone will show up in the wound.
Transverse fracture. A horizontal fracture line is common in this type of fracture. The fracture is oblique. This sort of fracture frequently has an angled pattern. Fracture that has been comminuted. The bone shatters into at least three pieces in this type of fracture.
The following are the most common causes of fractures:
Many fractures are painful and can prevent you from moving freely in the injured area. Other common signs and symptoms are:

Most people have likely hit their heads at some point. It can cause swelling or a minor headache, but the pain usually goes away on its own. Other times, if you don’t get medical help straight away, the injuries might become life-threatening.
How can you know where you fall on the spectrum? When should you go to the ER and when should you ice and take ibuprofen?
Any trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain is considered a head injury.The skull, for the most part, protects the brain from serious injury. However, with a catastrophic accident, the skull itself may break, exposing the brain to damage.
On the other hand, a person’s forehead may develop a tiny bump. However, it’s crucial to remember that, while injuries might vary in severity, it’s difficult to tell how serious an injury is merely by looking at it. You should never believe that you can just “tough it out” and wait for the pain to go away because complications from a catastrophic injury can lead to permanent impairment.
There are two primary methods to sustain a head injury: Trauma injuries are those that occur as a result of physical attack, sports-related accidents, falls, or motor vehicle accidents. Penetrating brain injuries, which are caused by trauma caused by a projectile such as a bullet or stabbing, are less common but just as fatal. Shaking: While these injuries are most prevalent in small children and newborns, they can happen to anybody who is shaken violently. Shaking a child or banging their head against a hard surface is referred to as Abusive Head Trauma (AHT).This causes the child’s head to move uncontrollably, shredding brain tissue and rupturing blood vessels as the brain moves back and forth. Furthermore, the movements may bruise the brain due to the numerous times it impacts the skull.
There are two main ways of experiencing a head injury: Trauma: These are injuries typically associated with physical assault, sports-related accidents, falls, and motor vehicle accidents. Less frequent but just as deadly are penetrating brain injuries, which are the result of trauma due to a projectile, such as a bullet or stabbing. Shaking: These injuries are most common in small children and infants, but can occur to anyone who experiences violent shaking. Also known as Abusive Head Trauma (AHT), it encompasses shaking a child or striking their head against a hard surface. This causes the child’s head to move uncontrollably, moving the brain back and forth, tearing brain tissue and rupturing blood vessels. In addition, the movements may cause the brain to become bruised from all the times it hits the skull.
When your head is wounded, bleeding on the surface or within the brain is a cause for concern because your head contains more blood arteries than other parts of your body. Because not all head injuries bleed, it’s crucial to be aware of the warning signs. Because many symptoms of a major brain injury may not present right away, it’s crucial to keep track of your symptoms for several days following your accident.
Minor Head Injury Symptoms
The following are some of the most common signs of a minor head injury:
Severe Head Injury Symptoms
Here are the most typical symptoms of a severe head injury:
Concussions, scalp wounds, and skull fractures are the most common head injuries. The degree of the damage and what caused it will determine the consequences and therapies. Open and closed head injuries are the two forms of head injuries. When your scalp and skull are broken, you have an opening, or piercing, injury. Any head injury that does not break your skull is considered a closed injury.
1. Concussions
A concussion is a severe brain injury caused by your brain being jolted back and forth too quickly, damaging brain cells, blood vessels, and neurons. If the hit to the head was severe enough, the brain may hemorrhage. They are most usually caused by head trauma, although they can also be produced by a forceful impact to the upper body.
Concussion Symptoms
Symptoms of a concussion include:
2. Cerebral Edemas
Edema is swelling caused by an excess of water in the tissues of the body. Cerebral edema (or edema of the brain) can occur as a result of head trauma or certain disorders, such as meningitis, encephalitis, or cancer, in the context of head injuries. Because it increases pressure inside your skull and obstructs blood flow to the brain, brain swelling can be fatal.
Brain Swelling or Edema Symptoms
Depending on the intensity of the swelling, edema symptoms might vary widely from person to person. These are some of them:
3. Diffuse Axonal Injuries
Axons are nerve cells’ tiny, threadlike fibers that transmit impulses to neighboring cells. Neurons are nerve cells that send and receive data throughout the body. Neurons in the brain can’t connect if axons are damaged, leading to degenerative disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. When a person’s brain changes inside the skull as a result of an injury, axons can be severed, putting the individual in a coma.
Diffuse Axonal Injury Symptoms
A person with a minor diffuse axonal damage may stay aware while experiencing a variety of symptoms, including:
4. Subdural Hematomas
A thick membrane that surrounds the brain and spinal cord is known as the dura mater. It is the outermost layer that protects the neurological system of a person. When blood pools beneath the dura mater following a head injury, it’s called a subdural hematoma. Increased pressure on the brain can result, potentially leading to unconsciousness or death. While this form of head injury can happen to anyone who takes blood thinners and receives a substantial blow to the head, it’s more likely to happen to people who use them.
Subdural Hematoma Symptoms
A person with a subdural hematoma may lose consciousness instantly in some cases. Symptoms may not appear for days, or even weeks, in some circumstances. These are some of them:
5. Brain Hemorrhages
When an artery in the brain ruptures, it causes a brain hemorrhage. This type of injury causes the death of brain cells in addition to the loss of blood. Trauma to the head, excessive blood pressure, a brain tumor, or an aneurysm can all cause this type of injury.
Brain Hemorrhage Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on how much brain tissue is injured, but they typically include the following:
6. Cranial Fractures
A crack or break in the skull is the result of this type of injury. Various types of cranial fractures exist: When the skin over the fracture isn’t broken, the fracture is closed. Open (when the skin breaks and the bone protrudes), Basal (damage to the base of the skull, behind the ears, nose, or back of the neck), and Depressed (injury to the base of the skull, behind the ears, nose, or back of the neck) are the three types of injuries (when the skull is indented).
Symptoms of Cranial Fracture
Did you know that heart disease is responsible for one out of every four deaths in the United States? It’s a devastating figure that illustrates the disease’s pandemic proportions.
It’s also a timely reminder to (a) learn to recognize the signs and symptoms of a heart attack, and (b) be proactive in making healthy lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of a heart attack. A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, is the leading cause of death in both men and women in the United States. Each year, around 1 million people in the United States suffer from one, with roughly half of them being deadly.
When blood supply to the heart is restricted, a heart attack ensues. A buildup of fat deposits, cholesterol, and plaque inside the arteries that provide blood to the heart causes the obstruction. The greater the level of cardiac damage, which can range from permanent damage to death, the longer the blockage continues. Significant quantities of stress or physical activity, both of which can cause the arteries to constrict, restricting blood flow, are other reasons for a heart attack.
There are many factors that increase the risk of a heart attack:
While certain aspects of having an autoimmune disease are beyond a patient’s control, many of the risk factors are directly tied to lifestyle choices. As a result, you can greatly reduce your risk of a heart attack by adding exercise into your daily routine, eating healthier foods, and stopping smoking.
You will have a far better chance of surviving a heart attack if you are aware of the signs. People who receive early medical attention have a survival rate of greater than 90%. Symptoms can differ; in fact, a person who has had a previous heart attack may have distinct symptoms if they suffer another one.
While some heart attacks are abrupt, many patients experience symptoms gradually. Someone who is experiencing one may not even be aware of what is going on. If you notice any of the indicators listed below, dial 911 right away. It’s preferable to have a false alarm than to risk death by waiting it out. Even if you think you’re awake enough to drive, call for assistance. On the journey to the hospital, your symptoms could increase, placing your life and the lives of other motorists in danger..
1. Shortness of Breath
This is one of the first symptoms, and it might occur weeks before a heart attack. It’s a cause for concern if you suddenly feel tired or exhausted despite not increasing your amount of physical activity.
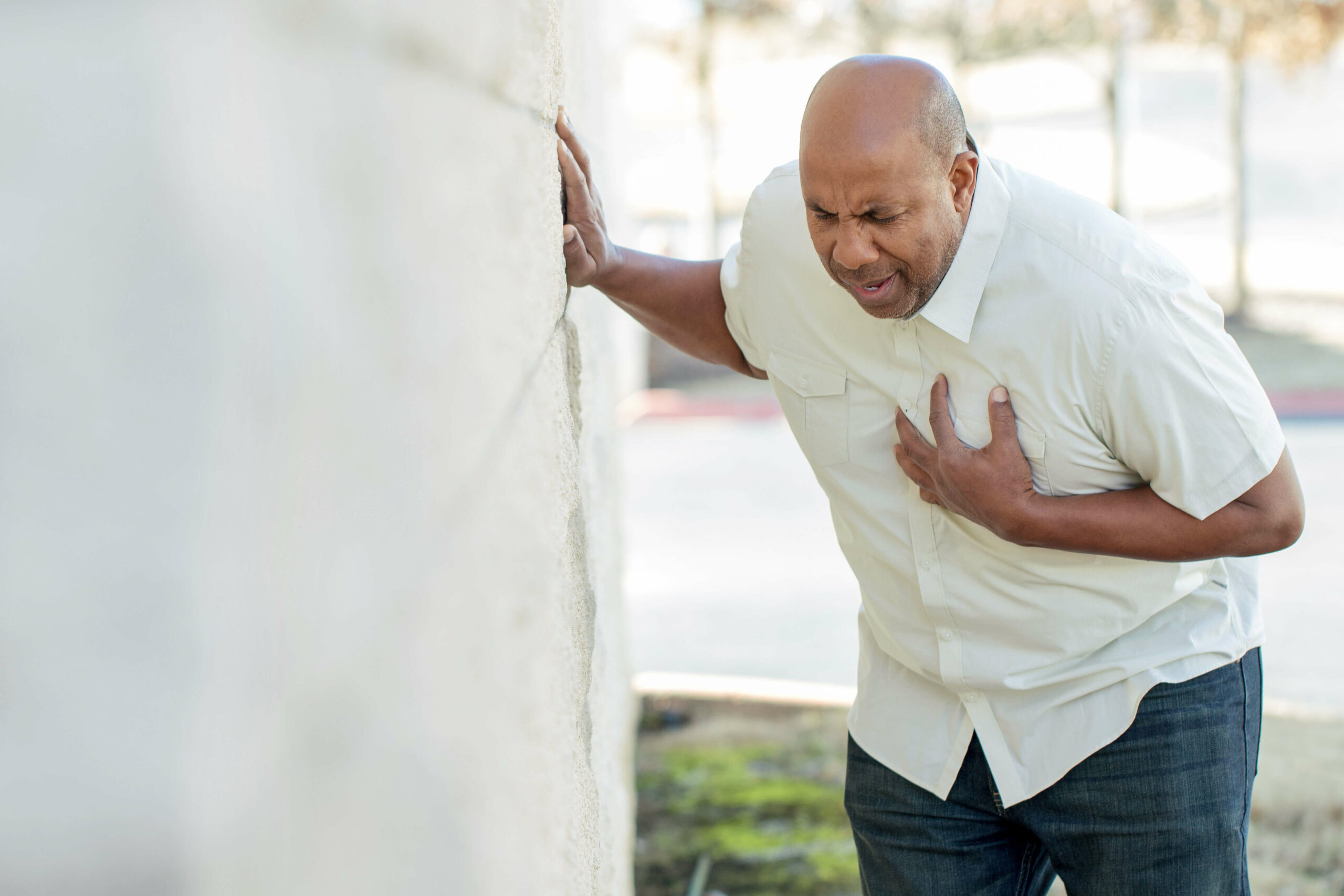
2. Chest Pain
It could be anything from a minor annoyance to severe agony. It may feel as if your chest is being crushed or as if pressure or weight is being applied to it. The pain or discomfort may come for a short time, then fade away before reappearing several hours later. Some people have no symptoms of chest discomfort at all.
3. Jaw Pain
Jaw discomfort that radiates to the teeth, neck, back, and down the left arm is common in people who are having a heart attack.
4. Pain in the Lower Abdomen
Women are more likely to experience this symptom.
5. Lightheadedness
Once you get up, this sensation becomes even more worse.
6. Cold Sweat
This occurs when the body is working excessively to ensure that the heart receives enough blood and oxygen.
7. Nausea
Keep in mind that this symptom does not affect everyone. Another thing to keep in mind is that, while taking aspirin can help prevent blood clots, it can also conflict with other medications you’re on, so let your doctor know if you’re on any form of prescription drugs.
If you fear you’re experiencing a heart attack, dial 911 for help right away!
If you have a heart attack, you must get medical help as soon as possible. If you have any cause to believe you are experiencing one, hurry to your local emergency center as soon as possible so that treatment may begin immediately.


The bacteria group A Streptococcus (group A strep) causes irritation and swelling of the tonsils and throat, resulting in strep throat. The cylindrical channel connecting your mouth to your windpipe and esophagus is known as your throat. The technical word for the throat is pharynx, which is why streptococcal pharyngitis refers to a sore and inflamed throat caused by a group A Streptococcus infection. Streptococcal tonsillitis is another name for strep throat (inflammation of the tonsils).
The majority of sore throats are caused by viral illnesses, while strep throat is the most prevalent bacterial cause. When left untreated, strep throat can lead to more significant health concerns in other parts of the body. Bacterial colonies can enter the kidneys, heart, and other organs. Quick diagnostic tests are performed to determine whether a sore throat is caused by group A Streptococcus, allowing for prompt antibiotic treatment. Strep throat is contagious and spreads quickly. Although it is more common among youngsters, the virus can be passed on to anybody through airborne particles. Red, inflamed, and swollen tonsils, as well as a sore throat, are typical strep throat symptoms. White pus patches on the tonsils are not uncommon as well . In addition, fever, headaches, and swallowing difficulty are some of the other symptoms.
People in excellent health can recover from strep throat at home by taking prescribed antibiotics as advised. Additional treatment may involve steps to help relieve symptoms and to keep the body as healthy as possible in order to reduce the risk of acquiring new difficulties. Drinking enough liquids, taking medications to relieve physical pains and fevers, and resting are all examples of self-care measures.
Antibiotics prescribed by a doctor are essential to treat strep throat. If you have strep throat symptoms such as fever and sore throat, or if you have increased swelling of the tonsils, or if you have a diagnosed case of strep throat that is not improving with medications, seek medical help right away. More acute strep throat complications, such as rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease, can be life-threatening in rare situations. If you or someone you’re with is having trouble breathing, swallowing, or has a change in awareness or alertness, seek medical help right away (phone 911).
We’ve all had the sensation of our heart skipping a beat, and it’s usually nothing to worry about if it happens only once in a while. However, you may have an arrhythmia if your heart is frequently racing, fluttering, or beating slowly.
An arrhythmia is a condition in which the heartbeat or rhythm is abnormal, impairing cardiac function and blood flow. The average human heart beats 60 to 100 times each minute. Anything quicker or slower than that could be a sign of a cardiac problem. Normal circumstances such as stress, sleep, and exercise can cause your heart rate to fluctuate without causing any problems.
Arrhythmia does not always mean danger. However, it can sometimes stop blood flow in the body, depriving your internal organs of oxygen and nourishment. It can cause you to pass out and even injure you when you fall. Arrhythmia can also be a sign of an underlying cardiac disease, leading to a heart attack or stroke.
When our heart’s electrical impulses are out of whack, we experience arrhythmia. A pulse usually starts in the sinoatrial node (SA node), which is located in the upper right chamber of our heart. The atria contracts in response to the signal. The atrioventricular node (AV node), which connects the atria (upper chambers of the heart) with the ventricles, receives the electrical impulse (bottom chambers of the heart). The signal directs the ventricles to contract and carry blood to the rest of our body once it has been slowed.
Arrhythmias can be caused by any variation from this line of events, including:
The two most common kinds of arrhythmia are:
1. Tachycardia: Fast heartbeat.
2. Bradycardia: Slow heartbeat.
There are, however, numerous more types of arrhythmia, such as:
Atrial fibrillation: Fast, irregular heartbeats that begin in the atria and may lead to a stroke.
Atrial flutter: Fast, regular heartbeats that begin in the atria that can progress to atrial fibrillations or strokes.
Heart block: The electrical signals between the SA node and the ventricles are slowed or stopped, resulting in a Stokes-Adams attack with fainting, convulsions, or death.
Long QT syndrome (LQTS): Fast, and very irregular heartbeats caused by congenital heart disease or medication, which can result in fainting, convulsions, and death.
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT): Fast heartbeats, generally 130 to 230 beats per minute, that originate in the atria.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS): Standing up causes a rapid acceleration of the heartbeat, which can cause fainting.
Premature atrial contractions (PACs): Extra heartbeats in the atria that normally do not create any health issues.
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs): Extra heartbeats in the ventricles, which are mainly triggered by caffeine use and aren’t life-threatening unless they’re paired with other arrhythmias.
Sick sinus syndrome/sinus node dysfunction: Due to scarring, the SA node malfunctions, resulting in bradycardia or a combination of slow and rapid heartbeats.
Ventricular fibrillation: Fast and irregular heartbeats, sometimes as fast as 300 beats per minute, begin in the ventricles and can swiftly lead to death.
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach): The volume of blood pumped through the body is reduced by fast and regular heartbeats that originate in the ventricles.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: Being born with a second channel between the atria and ventricles, in addition to the AV node, which causes a racing heart and pain.
Many forms of arrhythmia can be diagnosed and treated by doctors. They can use an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) or a portable Holter or event monitor to supervise your heart’s electrical impulses at home. They can also use ultrasound technology to look at the inside shape of the heart with an echocardiogram (echo).
If an abnormality is discovered, they may suggest the following actions:
A sudden change in heartbeat can be alarming, especially if you’ve never experienced it before. Always play it safe when it comes to heart health. If you’re experiencing a racing heart, drop in blood pressure or chest pain, come into the Complete Care emergency room nearest you. We are equipped to handle major medical emergencies, such as irregular heartbeat, heart attack, and stroke-like symptoms, and are open 24/7 to help you.

A stroke may strike anybody at any moment, especially an elderly person. Time is of the utmost importance when a stroke occurs. The earlier a stroke victim receives care, the better.
A stroke is a condition in which blood flow to the brain is disrupted, resulting in the loss of brain function. Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are the two kinds of strokes. A shortage of blood supply to the brain causes ischemic strokes. A buildup of blood in the skull causes hemorrhagic strokes. As a result, the brain’s damaged portion will stop working correctly. Strokes are a frequent and dangerous health problem that affects people of all ages. The majority of strokes occur among seniors, particularly those who are already in poor condition. Strokes, on the other hand, can strike even young and seemingly healthy persons.
Get Free Medical Consultation
Need help?