Aether Health - Kingwood ER is your trusted destination for emergency head injury treatment in Kingwood, Texas. When it comes to emergency treatment, every second counts, and our dedicated team of professionals is here to provide you with exceptional care when you need it most.

Head injuries can occur due to various factors and situations. Understanding the common causes of head injuries can help raise awareness and promote preventive measures.
Some of the common causes include:
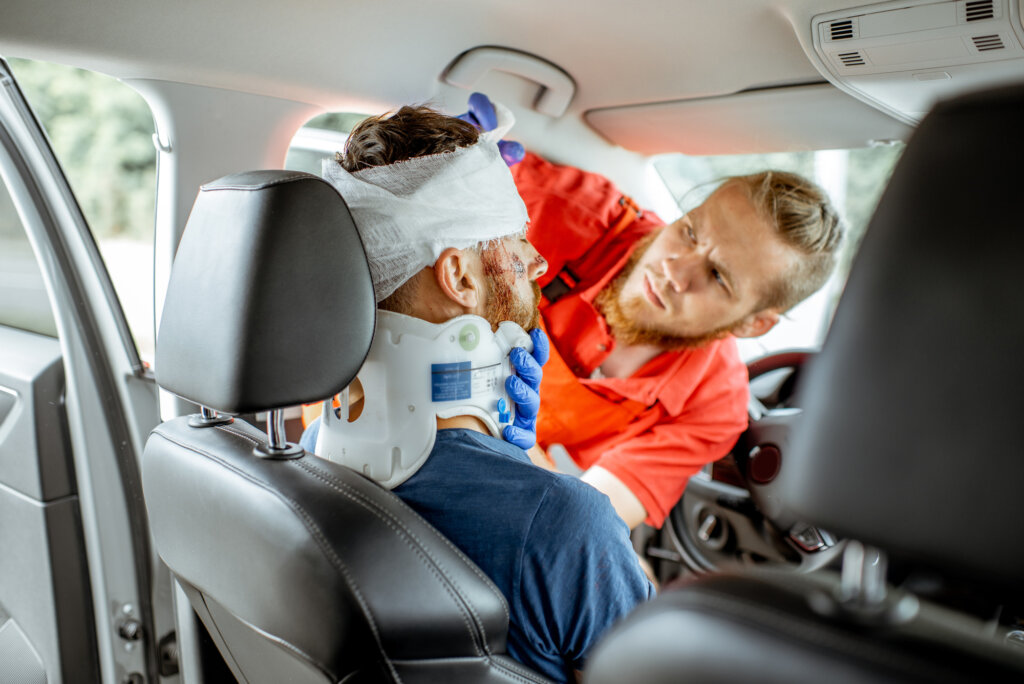
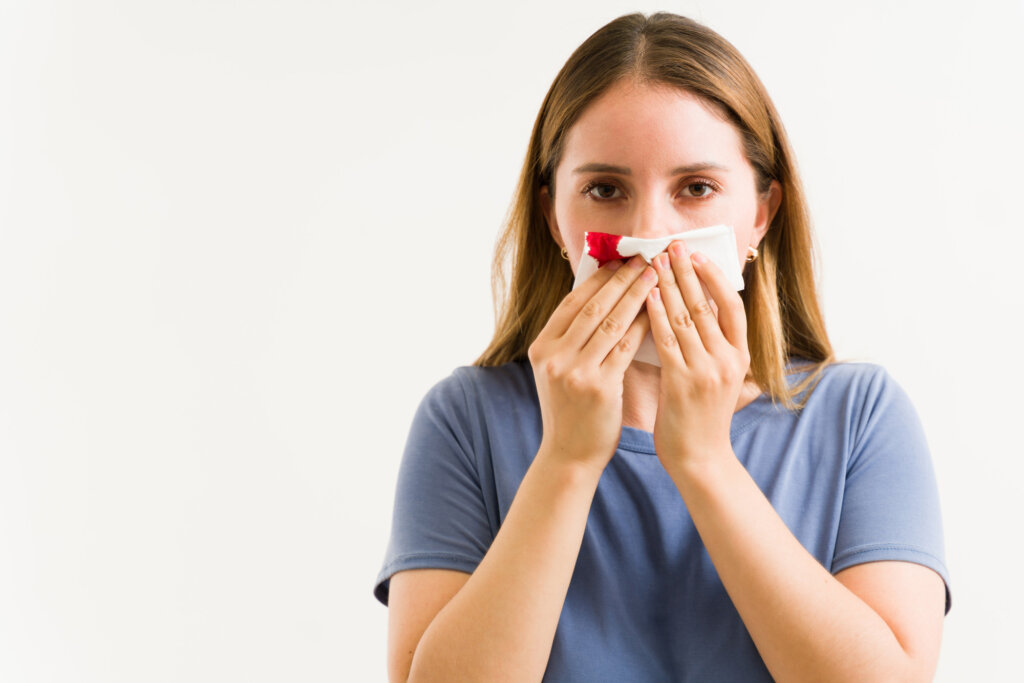
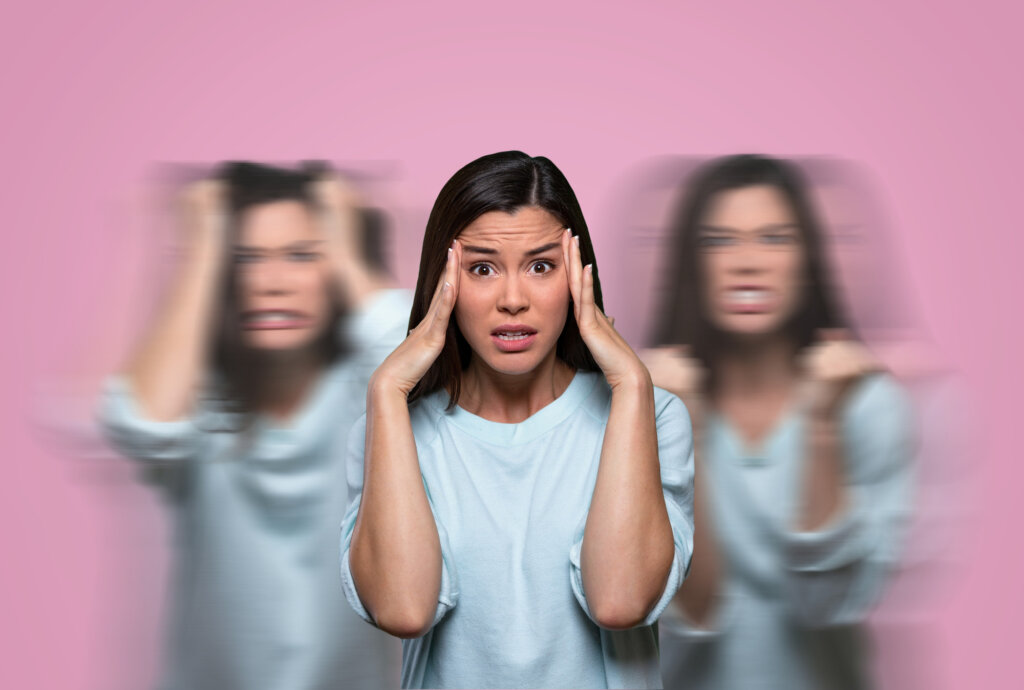
















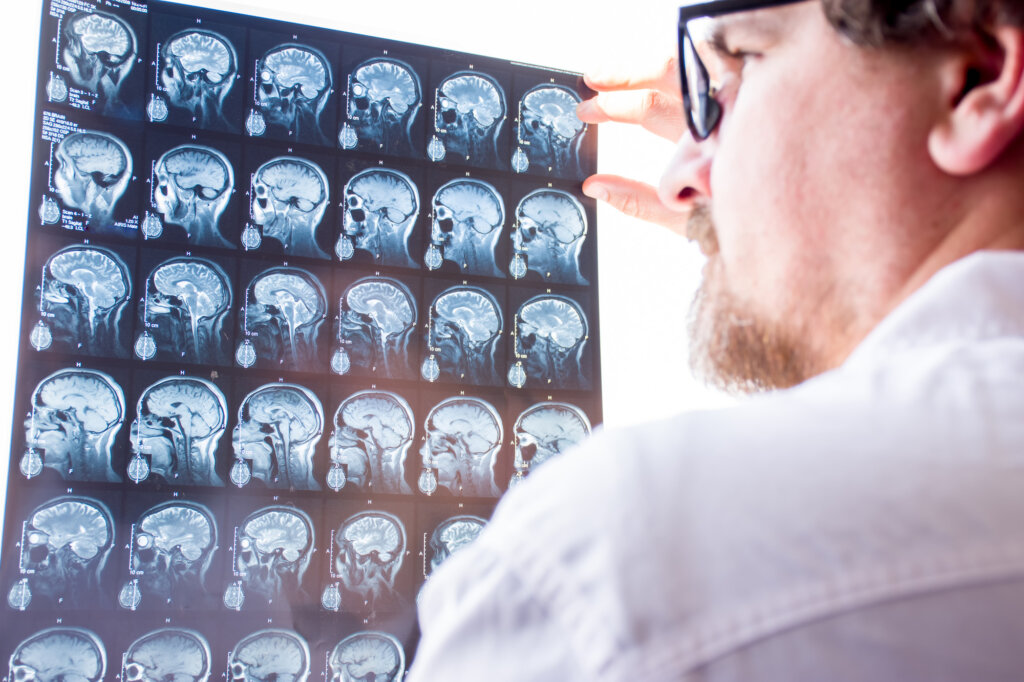
Proper diagnosis of a head injury is crucial to determine the severity and appropriate treatment. At Aether Health – Kingwood ER, our experienced medical professionals employ various diagnostic techniques to evaluate head injuries. The diagnostic process may include:










Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can.