A bladder infection may cause discomfort and pain if not treated promptly. While many health conditions may have simple and easy-to-do home remedies, a bladder infection may not be one of them.
Find out the signs and symptoms of a bladder infection and when to seek medical emergency care in this article.
What’s the Importance of an ER Visit for Bladder Infection?
While many cases can be managed with timely intervention and proper care, certain symptoms need urgent medical attention. Severe pain, high fever, or signs of a possible kidney infection should not be overlooked.
A visit to the ER can easily diagnose your condition and prevent possible complications that come with it. You will also have immediate access to treatment and to an emergency team ready to help you with recovery.
What is a Bladder Infection?
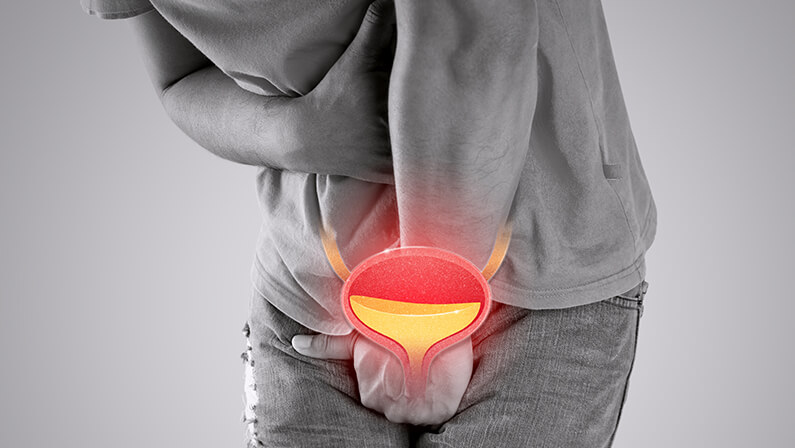
A bladder infection, also known as cystitis, is a common urinary tract infection characterized by the inflammation of the bladder. Typically caused by bacteria entering the urethra and multiplying in the bladder, this condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and various urinary symptoms.
What are the symptoms of a bladder infection?
There is a difference between UTI and bladder infection. Here are the warning signs:
- Frequent Urination: A bladder infection often causes an increased urge to urinate as the inflamed bladder becomes more sensitive.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or a burning sensation during urination is a hallmark symptom of cystitis.
- Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Changes in the appearance and odor of urine can signal the presence of infection, indicating the need for further evaluation and treatment.
What causes bladder infections?
- Bacterial Invasion: The most common cause of bladder infections is the entry of bacteria, usually Escherichia coli (E. coli), into the urinary tract.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Structural issues in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can contribute to infection risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Practices like incomplete bladder emptying, improper hygiene, or the use of certain contraceptives may increase susceptibility to bladder infections. Understanding these causes empowers individuals to take preventive measures and maintain urinary health.
Typical Treatment for Bladder Infections

Effective treatment for bladder infections involves a combination of medication and lifestyle adjustments. The common approaches include:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to eliminate the bacterial infection causing cystitis.
- Pain relievers: To alleviate discomfort during urination and reduce pain.
- Increased fluid intake: Promotes flushing out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Rest and self-care: Vital for supporting the body’s natural healing process and preventing complications.
When to Consider the Emergency Room for Bladder Infection
One thing you may ask yourself is: Should I go to ER for bladder infection?
Recognize the need for immediate medical attention if you experience the following:
- High fever: If you develop a high fever in conjunction with a bladder infection, it may indicate a more severe systemic infection requiring emergency attention.
- Severe pain: Intense and persistent pain in the pelvic or lower abdominal region suggests a potential complication that warrants a visit to the emergency room.
- Bloody or cloudy urine: Unusual changes in urine color or clarity could signal a more serious infection or underlying issue, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.
- Vomiting and dehydration: Persistent vomiting, coupled with signs of dehydration, indicates a need for urgent medical care to address the potential complications associated with a severe bladder infection.
- Failure to improve with antibiotics: If symptoms persist or worsen despite antibiotic treatment, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical attention to reassess the infection and explore alternative interventions.
- Elderly or immune-compromised individuals: Vulnerable populations may experience more severe consequences of a bladder infection, making it essential for them to seek prompt medical care if symptoms arise.
- Suspected kidney infection: Signs such as flank pain, fever, and systemic symptoms may indicate a progression to a kidney infection, requiring immediate attention in the emergency room.
- Pregnant women: Bladder infections during pregnancy can pose risks to both mother and baby; therefore, any symptoms should be promptly evaluated in an emergency setting to ensure the well-being of both.
What to Expect in the ER

Prepare for a comprehensive evaluation during a bladder infection emergency room visit. This includes a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as a urine test to identify infection and blood tests to assess overall health.
In some cases, imaging studies like a CT scan to pinpoint the extent of the infection or rule out other complications.
The medical team will work efficiently to provide accurate diagnosis and determine the most effective course of treatment based on the findings.
Preventing Bladder Infections
Implementing these bladder infection prevention measures can significantly reduce the risk of recurring infections and promote overall urinary health.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake helps flush out bacteria and toxins from the urinary tract, reducing the likelihood of infection.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintain proper genital hygiene, wiping from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the introduction of bacteria into the urethra.
- Urinate Regularly: Avoid holding in urine for extended periods, as this can create a breeding ground for bacteria in the bladder.
- Empty Bladder Completely: Ensure thorough emptying during each bathroom visit to minimize the residual urine that may harbor bacteria.
- Choose Showers Over Baths: Showers are preferable to baths, as sitting in bathwater can increase the risk of introducing bacteria into the urethra.
- Cranberry Products: Incorporate cranberry juice or supplements into your diet, as they may help avoid bladder infection,
Taking Charge of Your Bladder Health
Arming yourself with knowledge about bladder infections empowers proactive prevention and early intervention. By implementing preventative measures and recognizing the importance of prompt medical attention in specific situations, you can safeguard your urinary health.
If you experience symptoms warranting urgent care, don’t hesitate to visit Aether Health – Kingwood ER in Kingwood, Texas. Our experienced medical team is dedicated to providing swift and comprehensive care for bladder infections. Trust Aether Health for your emergency medical needs.