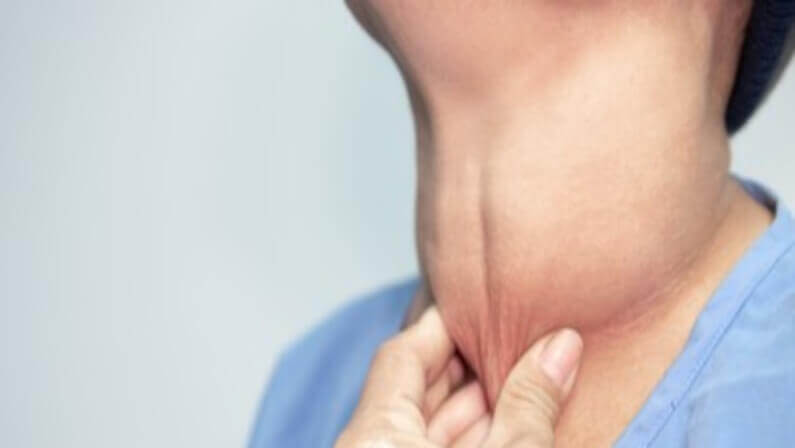
Thyroid disease is a common medical condition that affects the body’s ability to produce and regulate hormones, which play an important role in many bodily processes. The most common type of thyroid disease is hypothyroidism, which occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones.
Here’s what you need to know if you want to learn more about thyroid disease or think you may have it.
What is the Thyroid?
The thyroid is an endocrine gland located in the neck. It is responsible for producing two main hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are necessary for proper growth and development, as well as regulating metabolism.
Moreover, they help regulate the body’s energy level, temperature, and digestion. People with thyroid disease may experience fatigue, weight gain or loss, increased sensitivity to cold or heat, changes in appetite, and joint pain.
What does the thyroid do?
The thyroid is an endocrine gland located in the neck, just below Adam’s apple. It produces hormones regulating many bodily processes, including metabolism and growth. The two main hormones produced by the thyroid are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They are essential for proper growth and development, regulating the body’s energy level, temperature regulation, and digestion.
What is thyroid disease?
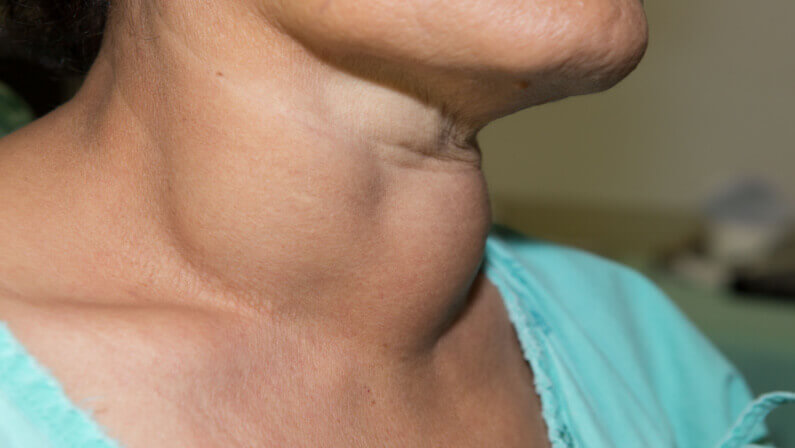
Thyroid disease is a condition caused by an imbalance in the production of thyroid hormones. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain or loss, hair loss, dry skin, anxiety, and depression.
Hypothyroidism is the most common type of thyroid disease caused by an underactive thyroid gland. This means that the thyroid does not produce enough hormones. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain or loss, increased sensitivity to cold or heat, changes in appetite, and joint pain.
Who is affected by thyroid disease?
People who are most at risk for developing thyroid disease include those with a family history of the condition, are postmenopausal, have recently given birth, are over age 70, or take certain medications.
Types of Thyroid Disease
There are eight types of thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiters, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, and more. Each of these conditions has different symptoms and causes and can be treated with lifestyle changes or medications.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is an overactive thyroid gland, which means it produces too many of the hormones T3 and T4. Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heart rate, irritability or anxiety, and difficulty sleeping. This condition can be treated with medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an underactive thyroid gland, which means it does not produce enough of the hormones T3 and T4. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, and feeling cold all the time. This condition can be treated with synthetic hormone replacement therapy or lifestyle changes such as eating a balanced diet and getting regular exercise.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
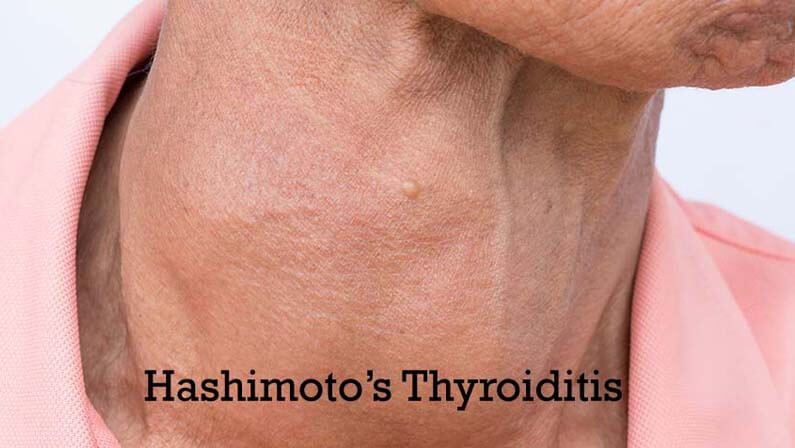
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own healthy thyroid tissue. This leads to inflammation and can cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain or loss, feeling cold all the time, and hair loss. Treatment usually involves taking synthetic hormone replacement therapy or other medications.
Thyroid Tumors
Thyroid tumors are abnormal growths in the thyroid gland. They can be benign or malignant, but most are not cancerous. Symptoms may include a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, and coughing up blood. Treatment for thyroid tumors depends on their type and size.
Thyroid Cancer
Once the tumors become malignant, they are considered thyroid cancer. Symptoms of this condition can include a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, and hoarseness. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Thyroid Disorders in Women
Women are more likely to develop thyroid disorders than men, due to hormonal changes throughout their life. Symptoms of thyroid disorders in women can include fatigue, weight gain or loss, and irregular menstrual cycles.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
This therapy is used to treat people who are not producing enough hormones due to an underactive thyroid gland. It involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3), which help to restore the balance of hormones in the body.
Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy
Pregnant women with hypothyroidism may experience complications, such as preterm labor, miscarriage, or gestational diabetes. It is important for pregnant women to get their thyroid levels checked regularly and to take synthetic hormone replacement therapy if necessary.
Postpartum Thyroiditis
This condition is caused by an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own healthy thyroid tissue after giving birth. It usually affects women who have had a baby within the last six months and can cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Treatment includes taking synthetic hormone replacement therapy or other medications as prescribed by your doctor.
Thyroid disease symptoms
There are different symptoms for each type of thyroid disorder, but some general symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain or loss
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Hair loss
- Feeling cold all the time
- Dry skin
- Sensitivity to heat
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty concentrating or thinking clearly
- Constipation
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
What causes thyroid disease?
The main causes of thyroid disease include autoimmune disorders, genetic factors, and environmental factors.
Such factors are:
- Autoimmune disorders: Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease can cause the body to attack its own healthy thyroid tissue.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic changes can increase the risk of developing a thyroid disorder.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain substances and radiation, such as perchlorate, can increase the chances of developing a thyroid disorder.
How is thyroid disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis of thyroid disease is based on physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Treatment depends on the type of thyroid disorder and may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
Some common treatments for thyroid disease include:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to measure certain hormones or proteins in the blood that can help diagnose thyroid disease.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can help to detect any abnormal growths in the thyroid gland.
- Physical Exam: A physical examination may be used to check for signs of an enlarged thyroid gland or other abnormalities.
- Thyroid Biopsy: A thyroid biopsy can help determine if a tumor is benign or malignant.
Is there a higher risk of developing thyroid disease if I have diabetes?
Yes, people with diabetes have an increased risk of developing thyroid disease. This is because the body’s immune system may be weakened by the effects of diabetes, making it more susceptible to autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease.
How is thyroid disease treated?
Thyroid disease can be treated through:
- Lifestyle changes
- Dietary changes
- Medication
- Surgery
Can I live a normal life with thyroid disease?
It can be hard to adjust to living with a thyroid disorder, but it is possible to live a normal life. Treatment can help to restore the balance of hormones in the body and minimize symptoms. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions to manage your condition and take prescribed medications. You can lead an active and productive life with proper management despite hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Living with a thyroid disorder can be challenging, so it is important to seek support and education from your doctor and family members. Support groups are also available to help you manage symptoms and learn more about living with a thyroid condition.
Should I exercise if I have thyroid disease?
Yes, exercise is important for people with a thyroid disorder. Exercise can help to regulate hormones, boost energy and improve mood. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program, as some types of activities may be too strenuous if you have an active thyroid condition.
It is also important to choose the type of activity that works best for you. Low-impact activities, such as walking and swimming, can be beneficial for people with thyroid disease.
Treat Thyroid Disease Today!
Thyroid disease is a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Knowing the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease is important, as it can help to diagnose and treat the condition early. It is also important to speak with your doctor if you think you may have a thyroid disorder so that they can recommend the right treatment for you. With the right care and treatment, people living with thyroid conditions can lead full and healthy lives.
We at Aether Health – Kingwood ER offer comprehensive evaluation and treatment services for thyroid disease. Our highly trained team of healthcare professionals is here to provide personalized care and support every step of the way. Contact us today to learn more about our services or to schedule an appointment.