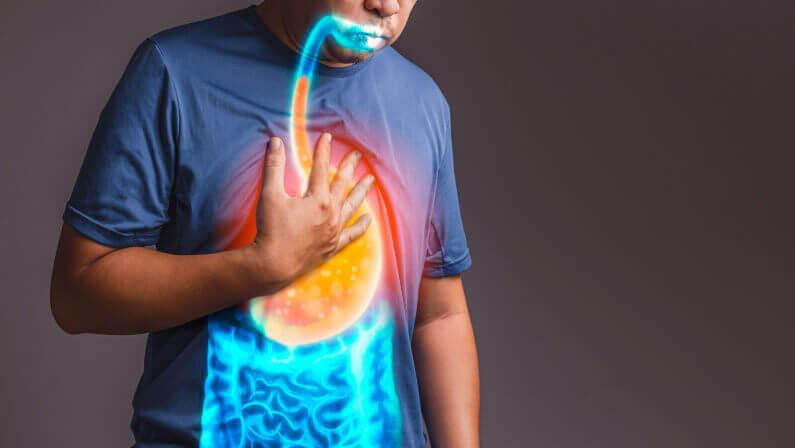
If you’ve been dealing with frequent heartburn, chest discomfort, or a sour taste rising in your throat, you might be wondering how long GERD lasts and whether it eventually goes away. The honest answer is that GERD is usually a long-term digestive condition, but the length of individual episodes depends on what triggered them and how quickly you intervene. Some flare-ups last only minutes to hours, while others may stretch over days or even weeks, especially if underlying triggers are not managed.
GERD tends to behave differently for every individual, so understanding its patterns is important for knowing what to expect and how to control its duration. The guide below breaks down how long GERD lasts in adults, infants, flare-ups, nighttime episodes, post-meal reflux, chest pain, and untreated cases—along with practical steps that help shorten these episodes.
What Is GERD and What Causes It?
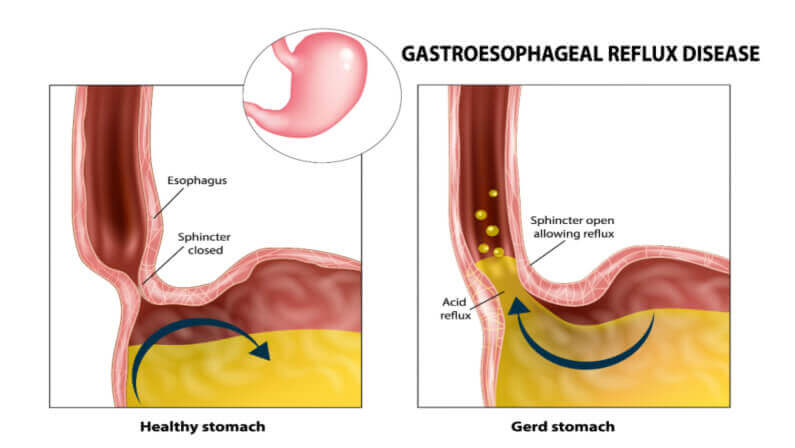
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, more commonly known as GERD, occurs when stomach acid repeatedly flows upward into the esophagus. This happens because the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)—a muscular valve meant to keep food and acid down—becomes weak or relaxes when it shouldn’t.
When this barrier fails, the lining of the esophagus becomes irritated, leading to heartburn, regurgitation, and other discomforts. While the condition itself is chronic, the intensity and duration of symptoms vary widely from person to person.
Several factors can trigger or worsen GERD, including large meals, lying down soon after eating, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, certain medications, and foods such as caffeine, chocolate, spicy meals, alcohol, and fatty dishes. Genetics can also play a role, making some individuals naturally more prone to reflux.
Common Symptoms of GERD
Symptoms often come and go, but when they appear, they tend to follow a recognizable pattern:
- A burning sensation in the chest (heartburn), especially after meals
• Regurgitation of sour or bitter-tasting fluid
• Chest discomfort that can mimic heart-related issues
• Difficulty swallowing
• Chronic coughing or throat clearing
• Hoarseness
• A persistent bitter or acidic taste in the mouth
• Bad breath due to ongoing throat irritation
GERD symptoms can be mild one week and intense the next, depending on diet, stress, sleep, and lifestyle habits.
What Are the Stages of GERD?
GERD generally progresses through four stages, depending on how often symptoms occur and whether the esophagus has been damaged.
Mild GERD
Occasional heartburn that does not interfere with daily routine.
Moderate GERD
More frequent symptoms, sleep disturbances, and increased discomfort.
Severe GERD
Daily symptoms with visible irritation or damage inside the esophagus.
Complicated GERD
Progressed cases involving strictures or Barrett’s esophagus due to long-term acid exposure.
Not everyone moves through all stages. Many individuals remain in the first two stages with proper management.
How Long Does a GERD Flare Up Last?
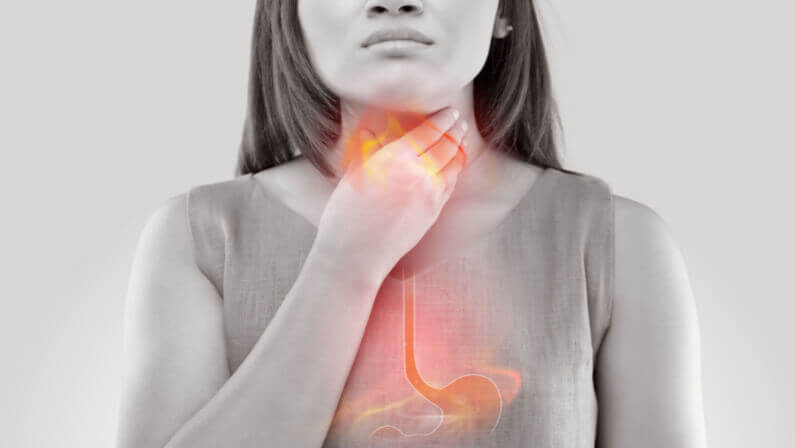
A GERD flare-up is usually a temporary phase of intensified symptoms triggered by something specific—such as a heavy meal, spicy food, stress, or lying down too soon after eating.
Most flare-ups last anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, but when irritation is more severe, the episode can linger for a few days. People who experience chronic reflux or repeatedly consume trigger foods may notice flare-ups lasting even longer. Staying upright, drinking water, avoiding irritants, and using antacids can help shorten the duration.
How Long Does a GERD Attack Last?
A GERD attack refers to a sudden surge of severe heartburn or chest discomfort. These episodes tend to last 20 to 60 minutes, but repeated attacks can make the discomfort feel longer. Attacks often intensify when someone is lying flat or bending forward.
Sitting upright, loosening clothing, and avoiding food immediately after an attack can help reduce its length and severity.
How Long Does GERD Last in Infants?
GERD in infants is common because their digestive systems are still developing. Babies often experience reflux after feeding, which can last 10 to 30 minutes per episode.
Most infants naturally outgrow GERD by 12 to 18 months as their sphincter muscles strengthen. Persistent symptoms beyond this age may require evaluation, especially if the child shows signs of poor weight gain, discomfort, or feeding difficulties.
How Long Does GERD Chest Pain Last?
Chest pain caused by GERD can be unsettling and is often mistaken for a heart-related issue. This discomfort usually lasts 30 to 90 minutes, and it tends to worsen after eating or when lying down.
If chest pain continues for several hours or feels unusual, it’s important to seek immediate medical care to rule out cardiac causes.
How Long Does GERD Last in Adults?
In adults, GERD is generally considered a chronic condition. While flare-ups come and go, the underlying tendency for acid reflux usually remains unless managed consistently. With proper lifestyle changes and medication, most adults experience significant improvement within several weeks, though some triggers may still cause occasional episodes.
Without treatment, GERD symptoms can persist for months or even years, often worsening over time.
Can Acid Reflux Last for Weeks?
Yes. Acid reflux can last for weeks if the esophagus remains irritated and if triggers continue unchecked. This prolonged inflammation may lead to complications, making early intervention important. Consistent treatment usually helps reduce symptoms within a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on severity.
How Long Does GERD Last at Night?
Nighttime GERD typically lasts 1 to 3 hours, mainly because lying flat allows acid to travel upward more easily. Eating too close to bedtime makes the problem worse and extends the duration. Raising the head of your bed, using extra pillows, and avoiding late meals can help significantly.
How Long Does GERD Last After Eating?
Post-meal reflux generally peaks within 30 to 60 minutes and gradually settles within 1 to 2 hours, depending on the size and type of meal. Larger meals or foods high in fat can prolong symptoms for 3 hours or more. Staying upright, walking lightly, and avoiding overeating can help shorten these episodes.
How Long Does GERD Last Without Treatment?
Without treatment, GERD can linger indefinitely. Symptoms may cycle through good and bad weeks, but the underlying issue rarely resolves on its own. Over time, untreated acid exposure can damage the lining of the esophagus and lead to complications such as strictures or Barrett’s esophagus. Early care helps prevent these long-term problems and improves daily comfort. If you are experiencing ongoing or severe gastro related issues, you can visit Kingwood ER for prompt care through our Gastrointestinal Emergency Services.
How Long Does It Take for GERD to Go Away with Medication?
With medication—especially proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)—most people notice gradual improvement within a few days, with full relief commonly achieved within 4 to 8 weeks. H2 blockers may work sooner for milder cases, but long-term management often requires a combination of medication and lifestyle changes.
Stopping medication abruptly may cause symptoms to return, so maintaining a consistent routine is important.
How Is GERD Diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually starts with a discussion of your symptoms and eating habits. If symptoms persist, your doctor may recommend:
- An endoscopy to examine the esophagus for inflammation
• pH monitoring to measure acid levels
• A barium swallow to observe reflux activity
• Manometry to evaluate how the esophagus muscles are working
These tests help confirm the diagnosis and identify any complications.
How Do You Treat GERD?
Treatment focuses on reducing acid exposure and strengthening the body’s natural defenses. This typically includes:
Lifestyle Adjustments
Eating smaller meals, losing weight if needed, limiting trigger foods, avoiding lying down after eating, and elevating the head during sleep.
Medications
Antacids for quick relief, H2 blockers for moderate symptoms, and proton pump inhibitors for long-term control.
Advanced Options
For individuals who do not respond to medication, surgical treatments may be considered to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux.
Potential Complications of GERD
If not addressed, GERD may lead to:
- Esophagitis
• Narrowing of the esophagus
• Breathing-related issues
• Barrett’s esophagus
• Chronic discomfort affecting sleep and daily functioning
Monitoring your symptoms and seeking timely care can help prevent these complications.
When to Seek Medical Care
While occasional reflux is common, persistent symptoms should be evaluated. If you experience severe chest pain, difficulty swallowing, or symptoms that continue despite home remedies and medications, prompt medical attention is essential.
If you are experiencing persistent GERD symptoms, frequent flare-ups, or severe chest discomfort, the team at Kingwood ER is available 24 hours a day to provide rapid evaluation, advanced diagnostic care, and immediate relief for digestive emergencies.
FAQs
How long can a GERD flare-up last?
Anywhere from several hours to a few days, depending on triggers and management.
How do you calm a GERD flare-up?
Stay upright, drink water, avoid trigger foods, and use antacids if needed.
What are the four stages of GERD?
Mild, moderate, severe, and complicated, depending on symptoms and esophageal changes.
Can GERD cause nausea?
Yes, nausea is a common symptom due to irritation of the esophagus and stomach.
Can GERD go away on its own?
Flare-ups may ease temporarily, but the underlying condition typically requires ongoing management.