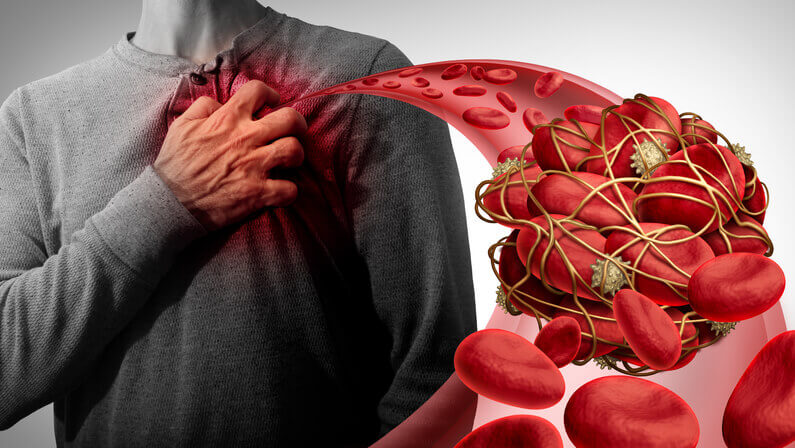
A blood clot is a serious medical emergency that can cause life-threatening health problems if not treated quickly. But what is a blood clot, exactly? What causes them, and how are they treated?
In this post, we’ll answer all your questions about blood clots. Stay tuned for information on the symptoms of a blood clot and how to get help if you think you might be experiencing one.
What Is a Blood Clot?
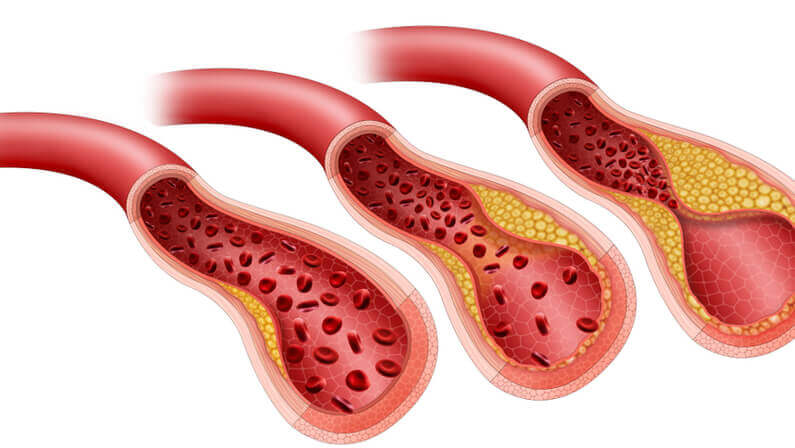
A blood clot (venous thromboembolism) is a clump of blood that has changed from a liquid to a gel-like or semisolid state. It’s a condition that includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins in the body while a PE occurs when a blood clot breaks off from a DVT and travels to the lungs.
Clots can occur anywhere in the body, but they most commonly form in the legs and arms.
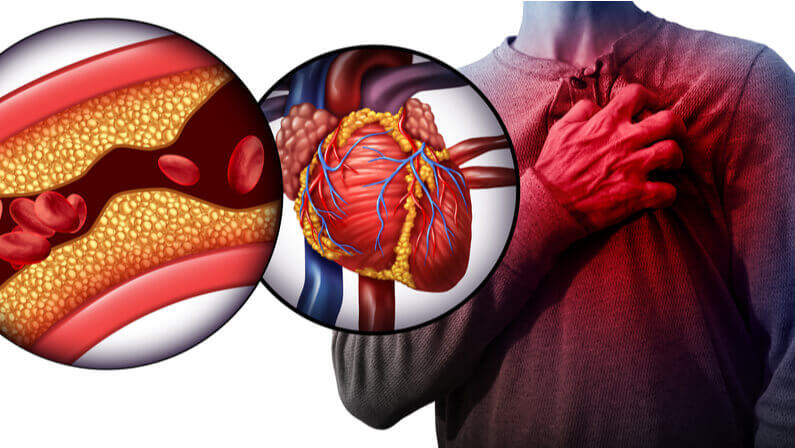
How Do You Know if You Have a Blood Clot?
There are a few blood clot symptoms that vary depending on the affected area.
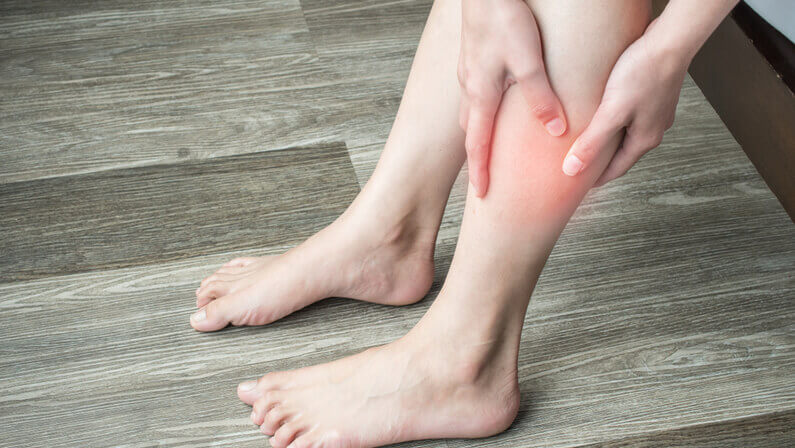
Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg or arm
- Sudden swelling in the affected area
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Warmth in the affected area
- Redness in the affected area
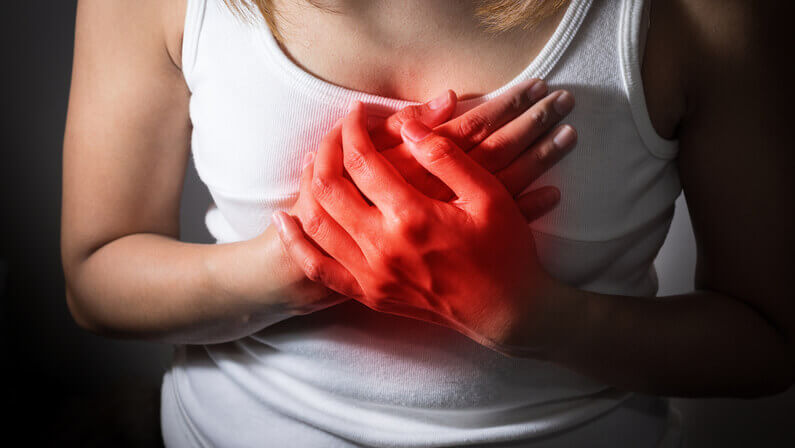
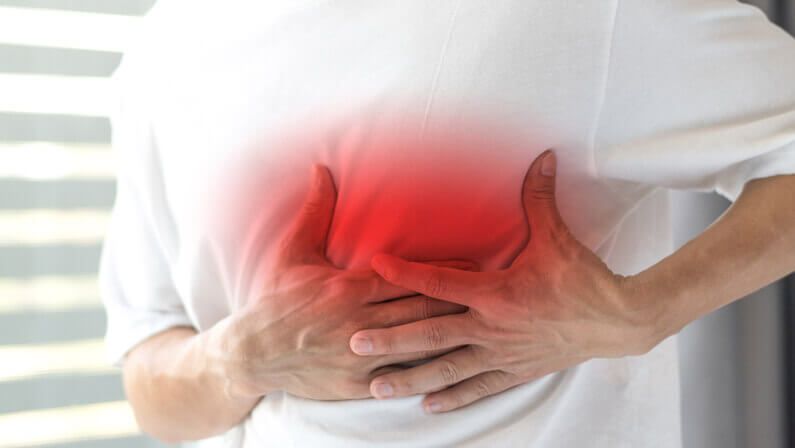
Symptoms of a blood clot in the heart (heart attack)
- Sudden chest pain or tightness
- Pain or discomfort in other areas of the body, such as the arms, back, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sweating
- Lightheadedness or dizziness

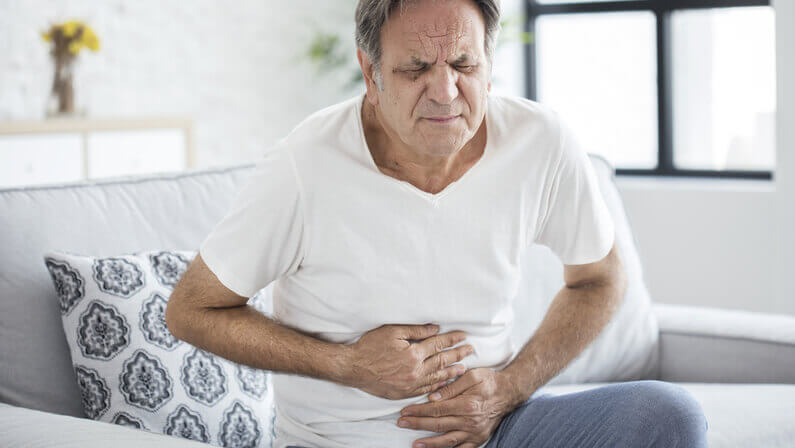
Symptoms of a blood clot in the abdomen (abdominal thrombosis)
- Sudden abdominal pain or swelling
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever or chills
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Blood in the stool or urine

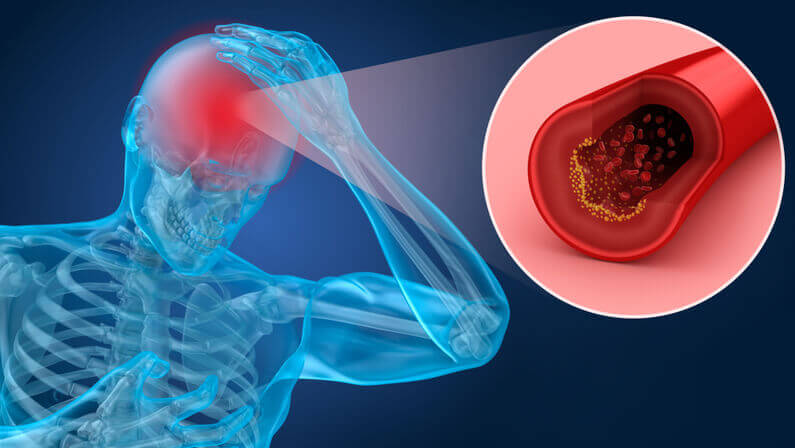
Symptoms of a blood clot in the brain (stroke)
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the body, typically on one side
- Confusion or difficulty speaking or understanding others
- Difficulty seeing or difficulty walking
- Severe headache or dizziness
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
Symptoms of a blood clot in the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or tightness
- Coughing up blood or bloody mucus
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Feeling anxious or restless
- Sweating or clammy skin
- Nausea or vomiting
If you experience any of these signs and symptoms, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention. It can be a serious medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Who Is at Risk of Blood Clots?
There are a few different factors that can increase your risk of developing a blood clot. These include:
- Age: The older you are, the greater your risk.
- Cancer: Cancer can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of clots.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy increases the risk of blood clots due to the changes in hormones and increased pressure on the veins.
- Hormone therapy: Taking certain medications, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of blood clots.
Other factors that can increase the risk of blood clots include genetics, obesity, regular periods of sitting or immobility (such as when traveling), and certain medical conditions such as diabetes.
What Are Causes of a Blood Clot?
There are several possible causes of blood clots, including:
- Injury to a blood vessel: This can damage the vessel’s lining and cause existing clots to form as part of the body’s natural healing process.
- Surgery: Surgery often involves cutting or damaging blood vessels, which can lead to the formation of clots.
- Hormone imbalances: Hormones play a crucial role in blood clotting, so changes in hormone levels can lead to the formation of clots.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes can damage blood vessels and lead to clotting.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause hormonal changes that lead to clotting, as well as increase the pressure on veins.
How Are Blood Clots Diagnosed?
Blood clots can be diagnosed through:
- Medical and family history: Your doctor will ask about your medical history, including any factors that may increase your risk of clotting.
- Physical exam: Your doctor will perform a physical exam to assess your risk of clotting, including checking for signs of swelling or redness in the affected area.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can be used to look for markers of clotting in the blood, such as a higher platelet count or an increased prothrombin time.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans can be used to take a closer look at the affected area and help determine whether a clot is present.
If you are diagnosed with a blood clot, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan. This may include medications to dissolve the clot or surgery to remove it. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make sure you understand all of your treatment options.
What Are the Types of Blood Clots
There are two main types of blood clots, including:
Arterial clot
An arterial clot is a type of clot that forms in an artery. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body, so an arterial clot can have serious consequences if left untreated. Some common risk factors for arterial clots include high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
Venous clot
A venous clot is a blood clot that forms in a vein. Veins are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart, so a venous clot is not as serious as an arterial clot. However, if left untreated, a venous clot can lead to complications such as pain, swelling, and skin ulcers. Some common risk factors for venous clots include sitting or standing for long periods, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions.
How Are Blood Clots Treated?
Blood clots can be treated with:
Medication
Medications can be used to dissolve blood clots or prevent them from getting worse. Some common medications used to treat blood clots include oral anticoagulants, aspirin, heparin, and warfarin.
Compression stockings
Compression stockings are special elastic garments that help to promote blood flow in the legs by applying gentle pressure to the veins. They can help prevent and treat venous clots.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot. This is usually only done if the clot is large or causing serious symptoms.
Stents
Stents are tiny metal tubes that are placed in the arteries to keep them open and help improve blood flow. They can be used to treat arterial clots that are causing symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
Vena cava filters
Vena cava filters are small devices implanted in the vena cava, or the main vein of the body, to prevent blood clots from traveling to the lungs. They are most commonly used in people who have had a blood clot in the leg or other parts of the body and are at high risk for developing another clot. Vena cava filters can help reduce the risk of serious complications such as a pulmonary embolism, while also allowing people to continue with their treatment plan.
How To Prevent Blood Clots
You can prevent blood clots by:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Quitting smoking
- Avoiding sitting or standing for long periods
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes and comfortable shoes
- Elevating your legs when you are sitting or lying down
- Talk to your doctor about any underlying medical conditions or other risk factors for blood clots that may be present in your case.
By following these simple tips, you can help reduce your risk of developing a blood clot. If you have any concerns or questions about blood clots, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider for more information and advice.
When To Go ER When Having Blood Clot
If you have any of the following symptoms, you should go to the ER:
- Sudden onset of shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort that worsens with deep breathing
- Sudden onset of coughing up blood
- Sudden onset of weakness, numbness, or difficulty moving one or more limbs
- Sudden onset of facial paralysis, particularly on one side
- Severe headache, dizziness, weakness, or confusion
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as they could be signs of a more serious condition. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and advise you of the best course of treatment based on your individual situation.

Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Blood clots can be scary, but with quick treatment, most people make a full recovery. If are in Kingwood, TX and you think you might have a blood clot, don’t wait to get help. Contact Aether Health – Kingwood ER right away and let us take care of you. We’re here to help 24/7.